What are M&A Data Rooms?
M&A data rooms are a secure location for storing documents and other materials prepared by a seller that a potential buyer can review. Typically, the seller designates a meeting room or office as a data room where the buyer and its advisors or attorneys access the documents, and the sellers and its advisors respond accordingly. In the past, those spaces were physically present. However, with the invention of cloud services, virtual M&A data rooms are increasingly employed alongside physical ones.
What are Physical M&A Data Rooms?
Using a data room is integral to the M&A due diligence process. Before taking the deal further, potential buyers should thoroughly review and analyse as much available information about the target company. On the other hand, in order to ensure security, the seller should disclose required documents sequentially only to the buyer’s authorised personnel. Additionally, the seller could grant access to only one preferred bidder instead of simultaneously revealing information to many potential traders for security. It is also required to continuously monitor that the exposed information does not leak outside the purpose of the investment. With the rise of cross-border M&A deals, due diligence costs could get high when potential buyers come from other countries. To effectively control the costs, the seller can use a virtual data room to allow the buyer to access the M&A data rooms remotely. That is one of the advantages of virtual M&A data rooms.
Through the M&A Data Rooms
Prospective buyers must analyse M&A data rooms information to capture opportunities and synergies from acquiring the target company. In addition, they need to identify potential inherent risks to identify ongoing or future issues before submitting a final bid. The seller should monitor the buyer’s access to the data room throughout the due diligence process. Here, the seller could track the buyer’s interests and activities and devise a marketing strategy accordingly.
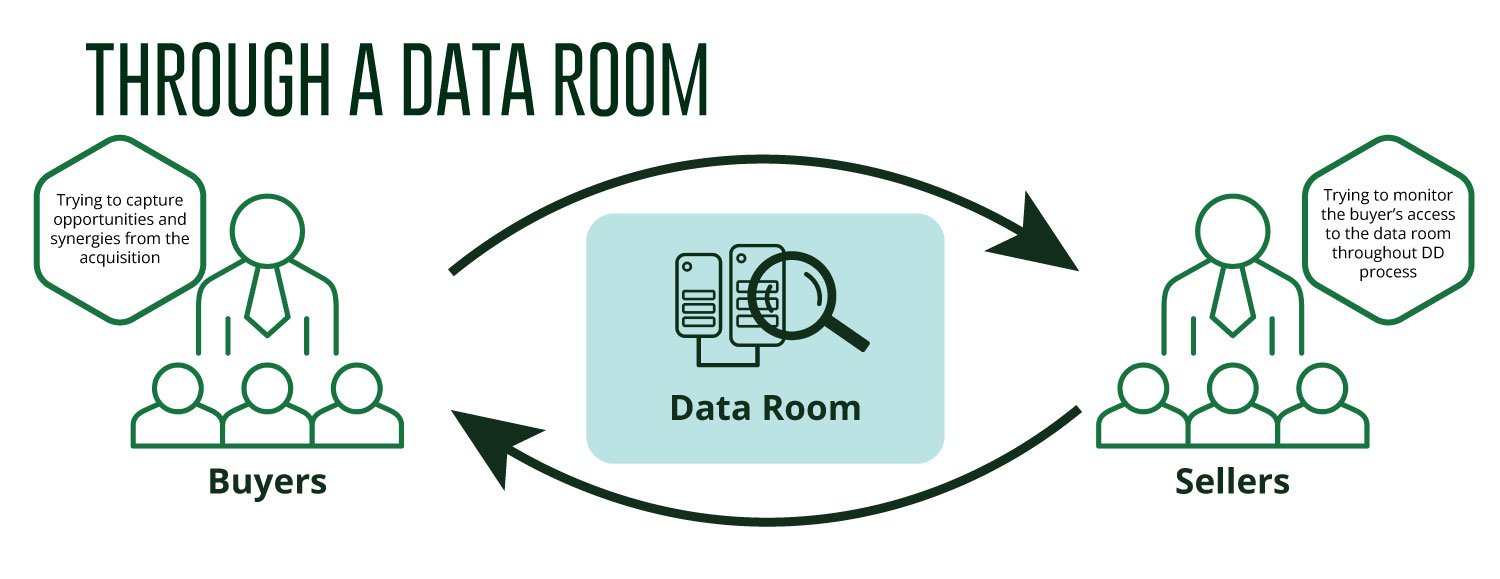
Due Diligence Response
During the data room analysis, potential buyers may request follow-up questions about data or new materials that go beyond the scope of the prepared documents. For them, the seller should respond in an orderly and timely manner. The amount and content of the data room could also be customised for individual bidders. For example, strategic buyers competing with the target company may not have access to sensitive competitive information.
What is an Virtual M&A Data Room?
A Virtual Data Room (VDR) is a cloud-based solution that securely shares confidential information. VDRs are commonly used in M&A deals or private equity investments to allow potential investors to access data through a secure internet connection. The advantages of VDRs over physical M&A data rooms include cost-effectiveness, ease of accessibility, and enhanced security measures. Standard features of VDRs include Q&A tools, note-taking capabilities, multi-factor authentication, and advanced permission settings. In response to growing online security concerns, VDR providers are continuously improving security features to maintain the integrity and confidentiality of data.
How are Virtual M&A Data Rooms used?
Virtual M&A data rooms are commonly utilised in M&A transactions, where buyers must access substantial amounts of confidential documentation to conduct their due diligence processes. The secretive nature of these documents necessitates their secure storage, which is only accessible to authorised bidders. VDRs provide a secure platform for exchanging and reviewing documents, eliminating buyers’ physical visits to the seller’s office. This approach enhances security and reduces costs associated with handling large paper documents or arranging multiple participants to scrutinise documents at different locations.
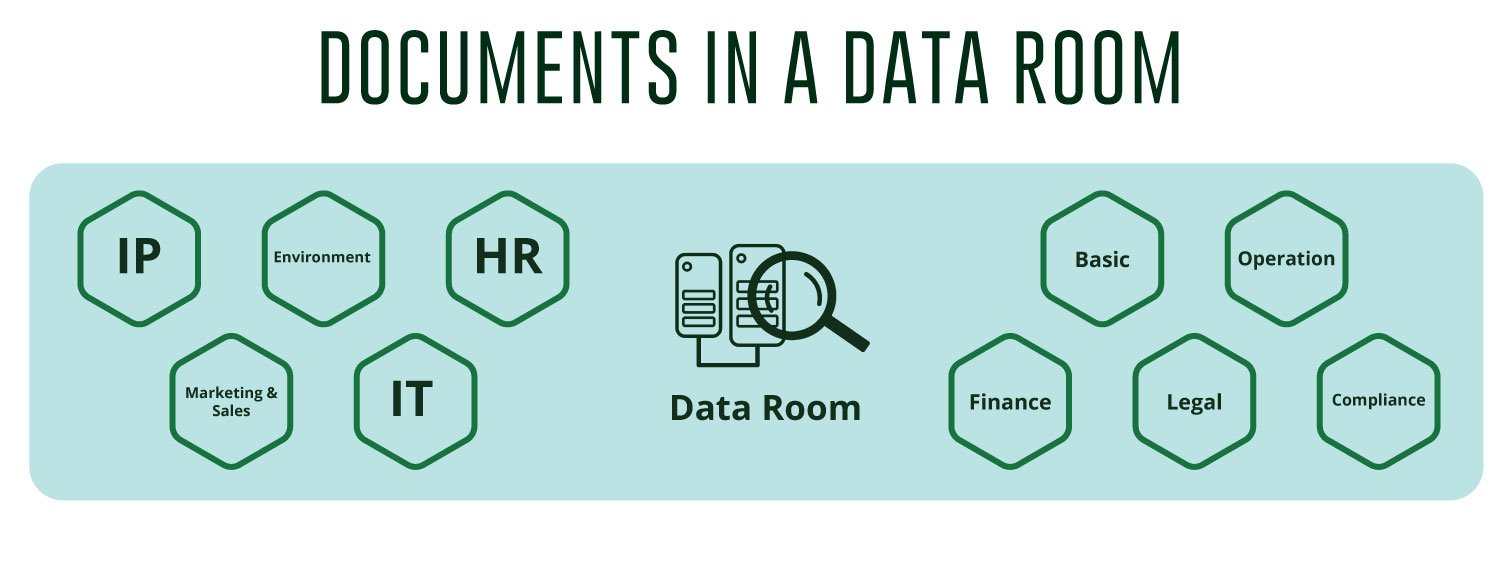
Documents Required for M&A Data Rooms
The specific documents required for due diligence in M&A can vary depending on the sector of the target company. However, some essential documents that are typically necessary across all industries include:
- Basic corporate Documents
- This includes articles of incorporation, bylaws, business plans, board and shareholder meeting minutes, and any other documents that provide insight into the structure and governance of the company.
- Operational information
- This includes the target company’s operations, production processes, supply chain management, customer data, and any other relevant operational data.
- Financial information
- This includes financial statements, financial projections, tax returns, accounts payable and receivable reports, tangible assets lists and market prices, and other financial data that provide insight into the financial health of the company.
- Legal information
- This includes corporate records, all the contracts with customers, suppliers, and employees, licenses, permits, unsolved litigation, and other legal documents related to the target company’s operations.
- Regulatory compliance
- This includes the target company’s compliance with applicable laws and regulations, including environmental, health and safety, and labour laws.
- Intellectual property
- This includes patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, know-how, and other intellectual property owned by the target company.
- Environmental data
- This includes the target company’s environmental impact, related laws, permits, reports, and other environmental data.
- Human resources
- This includes the organisation chart, executives’ or key employees’ profiles, employment agreements, compensation plans, and other documents related to human resources.
- Marketing and Sales Data
- This includes customers, market research, marketing materials, key salesforces and incentive systems, sales reports, and other relevant marketing and sales data.
- IT and cybersecurity
- This includes the target company’s IT infrastructure, internal ERP, cybersecurity policies, and other relevant technology-related data.
It’s important to note that these data room categories are not exhaustive and may vary depending on the specific industry. Additionally, the data room requirements may vary depending on the particular needs of the acquiring company and the scope of the M&A deal.
Level of M&A Data Rooms Access
Meanwhile, information in an M&A data room may have different access levels depending on their nature. To prevent excessive information leakage, the seller must differentiate the access level according to the counterparty and the degree of sincerity of the negotiations. We can divide them into three tiers like the following:
- Tier 1 – Information that can be released to all potential investors.
- Generally, those materials are not sensitive, so the seller primarily uses them for marketing when the deal is public.
- Tier 2 – Information that can be provided to serious bidders.
- Information herein may be sensitive to disclosure, so the seller provides them only to the preferred buyers through a secure data room during due diligence.
- Tier 3 The most critical and confidential internal information.
- They can be carefully submitted through the two parties’ agreement for specific requests.
These materials typically include the target company’s crucial know-how, customer lists, in-house technology, and other information that, if exposed, could affect the company’s performance.
Sources and Further Reading
If you have found the information insightful, head over to the M&A Institute, log in and start our online courses now. Or go to our Youtube Channel for further watching!
For further studying we recommend checking out:


