Demystifying Representations and Warranties in M&A Agreements
In our MAI‘s analysis of M&A Agreements, we delve deeply into the crucial aspects of representations and warranties, highlighting their essential role in ensuring the integrity and success of such transactions.
- We begin by exploring the concept of representations and warranties, elucidating their purpose and impact within the framework of an M&A deal.
- Next, we examine the intricate relationship between indemnities and representations and warranties in M&A transactions.
- The discussion then shifts to pre-transaction covenants, emphasizing their importance in maintaining the value of the deal amidst the complex dynamics of M&A processes.
- Our analysis also covers key focus areas in M&A contracts, identifying the crucial clauses and provisions that demand careful consideration.
- Finally, we conclude with an exploration of how securing M&A success involves strategic stability and collaboration.
Through this detailed exploration, this MAI blog aims to equip you with a comprehensive understanding of representations and warranties in SPAs.
What are Representations and Warranties?
Representations and warranties form the bedrock of M&A contracts. These legal constructs are not just jargon but are essential in delineating the factual and future assurances that underpin these complex agreements.
The Core of Representations
SPA representations are the factual backbone of any M&A agreement, offering a current snapshot of the company’s state of affairs. These include:
- Corporate Authority: A representation that confirms the company’s legal capacity to enter into the transaction, a non-negotiable in the realm of M&A.
- Intellectual Property: This crucial representation assures that intellectual property rights are clear and unencumbered, an especially vital aspect in tech-driven deals.
Warranties: The Promises Extending Into the Future
SPA warranties offer a safety net for the future, promising that the present conditions will prevail for a certain time after the contract is signed, such as:
- Duration and Assurance: A warranty might guarantee the flawless operation of a product for a future period, providing a safeguard against early failures.
- Remedies: It’s the warranty that spells out the recourse for breaches, ensuring the buyer is protected if the product doesn’t perform as promised.
Due Diligence and Representations: A Critical Interplay
Due diligence is the meticulous investigation preceding any M&A deal, with representations serving as guideposts. They inform the probing eyes of legal and financial experts and, if found to be inaccurate, can significantly alter the course of negotiations.
Distinguishing Representations from Warranties
While intertwined, representations and warranties serve distinct functions:
- SPA Representations: Offer a verifiable truth about the company’s current state.
- SPA Warranties: Ensure that the present conditions persist into the future, safeguarding the buyer’s investment.
The Strategy Behind Disclosures
Astute disclosure of representations and warranties can be a strategic move. By voluntarily disclosing issues upfront, along with remedial measures, a seller can foster trust and potentially negotiate more favourable terms.
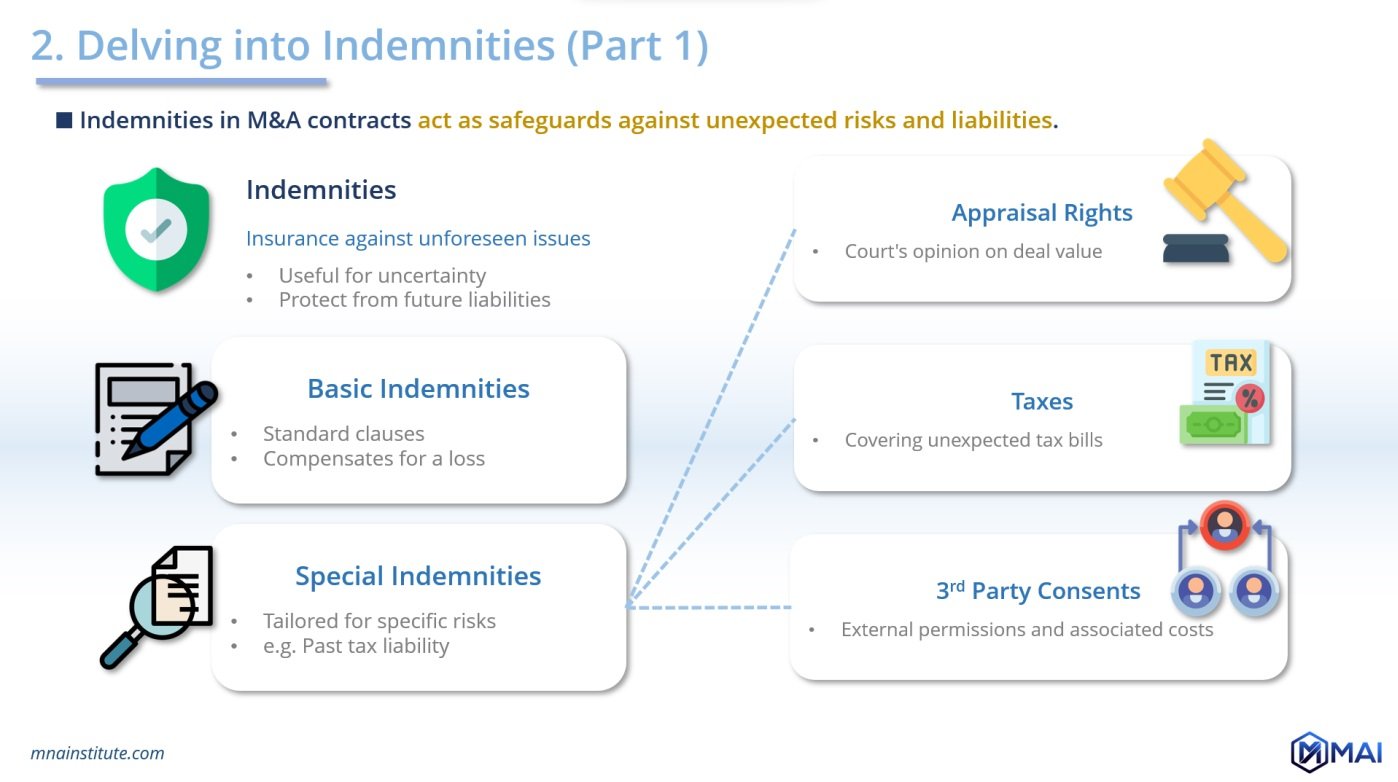
Indemnities and Their Interplay with Representations and Warranties in M&A
Indemnities in M&A contracts are critical clauses, intricately connected with representations and warranties, designed to protect parties from potential risks and unforeseen liabilities.
The Role of Indemnities in M&A Contracts
SPA indemnities are contractual promises that are often contingent on the clauses provided. They serve as financial protection for the parties, offering coverage for losses due to specific events or breaches related to representations and warranties.
Understanding Basic and Special Indemnities
- Basic Indemnities: These standard clauses come into effect if, for instance, the representations and warranties regarding asset ownership are found to be false.
- Special Indemnities: Tailored to specific risks, these are particularly important when due diligence uncovers unique risks, such as past tax liabilities.
SPA indemnities prove most valuable when there’s uncertainty about the representations and warranties provided, such as in the case of ongoing intellectual
Special Indemnities and Their Details
- Appraisal Rights: Here, indemnities may be linked to representations and warranties about shareholder equity, covering costs when valuation disputes arise.
- Taxes: Indemnities can address potential inaccuracies concerning the company’s tax history.
- Deal Expenses & Third-party Consents: Costs or liabilities arising from external permissions can be managed through special indemnities.
Temporal Aspects and Financial Mechanics
- Indemnity Survival Period: This period is often negotiated and defines the timeframe for indemnity claims.
- Deductible Basket: Set as a percentage of the sale price, this clause relates to the materiality of claims under representations and warranties.
- Damages Cap: A cap on indemnities, setting a maximum financial exposure level.
Escrow’s Role in Reinforcing Indemnities
To secure indemnity claims, parties may place funds in escrow as a part of the representations and warranties agreement, ensuring there’s a financial reserve to address any breaches.
Breaching Indemnities: Consequences
When SPA indemnities are breached, the repercussions are typically financial and substantial. The terms of these consequences are dictated by the original M&A contract’s representations and warranties clauses.
Pre-Transaction Covenants: Upholding the Value Amidst M&A
The journey from a signed M&A agreement to its close is safeguarded by covenants and commitments made by both parties.
The Pillars of Pre-Transaction Covenants
Pre-transaction covenants are essentially the guardrails that maintain the business’s value and operational integrity. These contractual promises stipulate the required conduct of both parties leading up to the closing of the deal.
Positive Covenants: Proactive Maintenance
These covenants involve actions that a party—typically the seller—must undertake, such as maintaining inventory levels or marketing efforts. They ensure that the business remains in the state as described in the representations and warranties section until the deal’s completion.
Negative Covenants: Ensuring Stability
Negative covenants restrict actions, like the seller incurring new debts, which could jeopardise the transaction’s financial stability.
Ordinary Business Operations Clause
This clause concerns the seller’s standard business practices. It mandates the seller to continue operating the business in the usual manner, thereby preserving the status quo referenced in the representations and warranties clauses.
Exclusive Dealings Provision
Similar to an engagement’s exclusivity, once an acquisition agreement is signed, the seller commits not to seek or accept offers from other potential buyers. This ensures the buyer can continue the acquisition process without fear of another bidder taking the target company.
In conclusion, pre-transaction covenants and commitments are vital components that ensure the representations and warranties are respected, serving to maintain the transaction’s agreed-upon conditions and business value during the transitionary phase of an M&A deal.
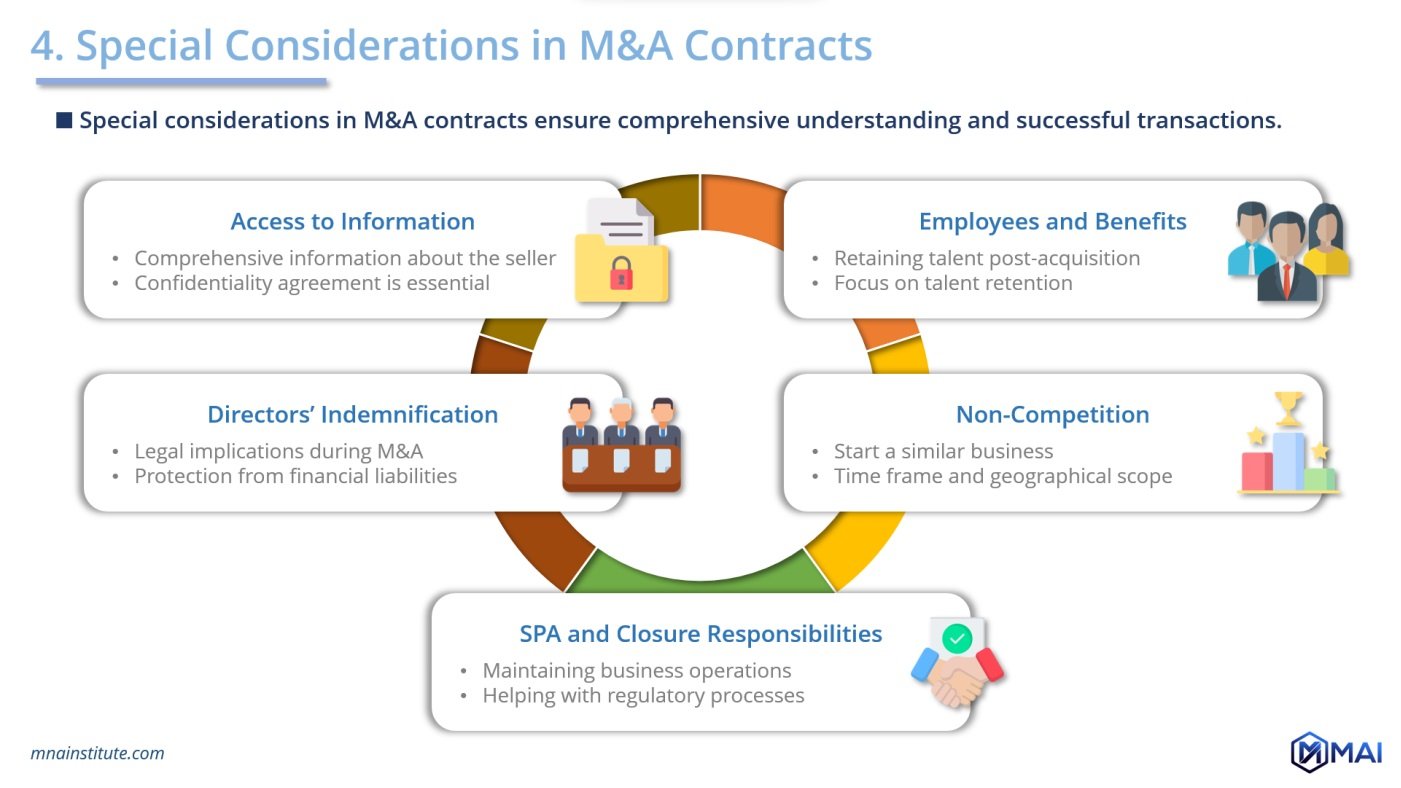
5 Key Focus Areas in M&A Contracts
While representations and warranties are crucial in M&A contracts, several other areas require meticulous attention to detail and strategic foresight.
Access to Information and Upholding Confidentiality
A successful M&A deal hinges on the buyer’s access to critical information, which must be balanced against the need for confidentiality. representations and warranties regarding the accuracy and completeness of this information are vital, but so too is the confidentiality agreement that governs the use and protection of the data shared.
Prioritising Employees and Benefits
Ensure that employee concerns are addressed and that their benefits are preserved or integrated with the acquiring company is often stipulated in the contractual provisions, safeguarding the human capital that is essential for the continuity of the business.
Directors’ and Officers’ Indemnification and Insurance
Representations and warranties also play a role in safeguarding the interests of the company’s directors and officers. Clauses that indemnify and insure them ensure that these individuals are not personally liable for their decisions made in the capacity of their corporate roles during the M&A process.
Enforcing Non-Competition to Safeguard Interests
To protect the investment, non-competition clauses are crucial. They ensure that the seller or key personnel do not use their industry knowledge and connections to compete with the business post-sale, within a defined timeframe and geographical area.
SPA: Ensuring Smooth Transition to Closure
The period between the signing of the SPA and the closure of the deal is often governed by representations and warranties about the seller’s responsibilities. These include maintaining the ordinary course of business and supporting the buyer with regulatory clearances to facilitate a smooth transition.
While representations and warranties form the backbone of trust in M&A contracts, it is these special considerations that often determine the success of a transaction. Addressing these areas with care ensures a thorough and effective M&A process, leading to a transaction that benefits all parties involved.
Securing M&A Success: Strategic Stability and Collaboration
A smooth M&A transaction hinges on the stable and uninterrupted operation of the target company during the transition period. Buyers place significant emphasis on the business’s continued performance, which is often underpinned by representations and warranties related to its operations.
Maintaining Business Conduct Until Closing
The interim between signing the M&A agreement and its final closure is critical. It’s during this time that representations and warranties regarding the company’s operations take center stage, assuring the buyer that no drastic changes will occur that could jeopardize the deal. Sellers are expected to steer clear of major shifts in business strategy or significant new projects that could alter the company’s trajectory or financial health.
Collaborative Efforts to Ensure Transaction Completion
Collaboration is a key theme in M&A transactions. The selling company commits, to exert reasonable efforts in aiding the buyer to secure necessary regulatory approvals. But it goes beyond compliance; it’s about maintaining open lines of communication, ensuring due diligence is thorough, and working together to address any complications that might arise.
Stockholder Approval: A Key Milestone
In deals involving publicly traded companies, stockholder approval is paramount. Representations and warranties about the company’s status and prospects form the basis for securing this consent. Clear, transparent communication that articulates the transaction’s logic and benefits is crucial in winning over stockholders, whose buy-in is crucial for the deal’s advancement.
As the M&A deal approaches its completion, proactive management, strategic foresight, and mutual cooperation are the linchpins of success. The representations and warranties provided serve as assurances that both parties will adhere to their commitments, ensuring that the transition period supports, rather than undermines, the ultimate goal of a successful merger or acquisition.


